Combining SafeKit High Availability with Disaster Recovery Backups
Synchronous SafeKit Replication for HA vs. Asynchronous Backup Replication for DR
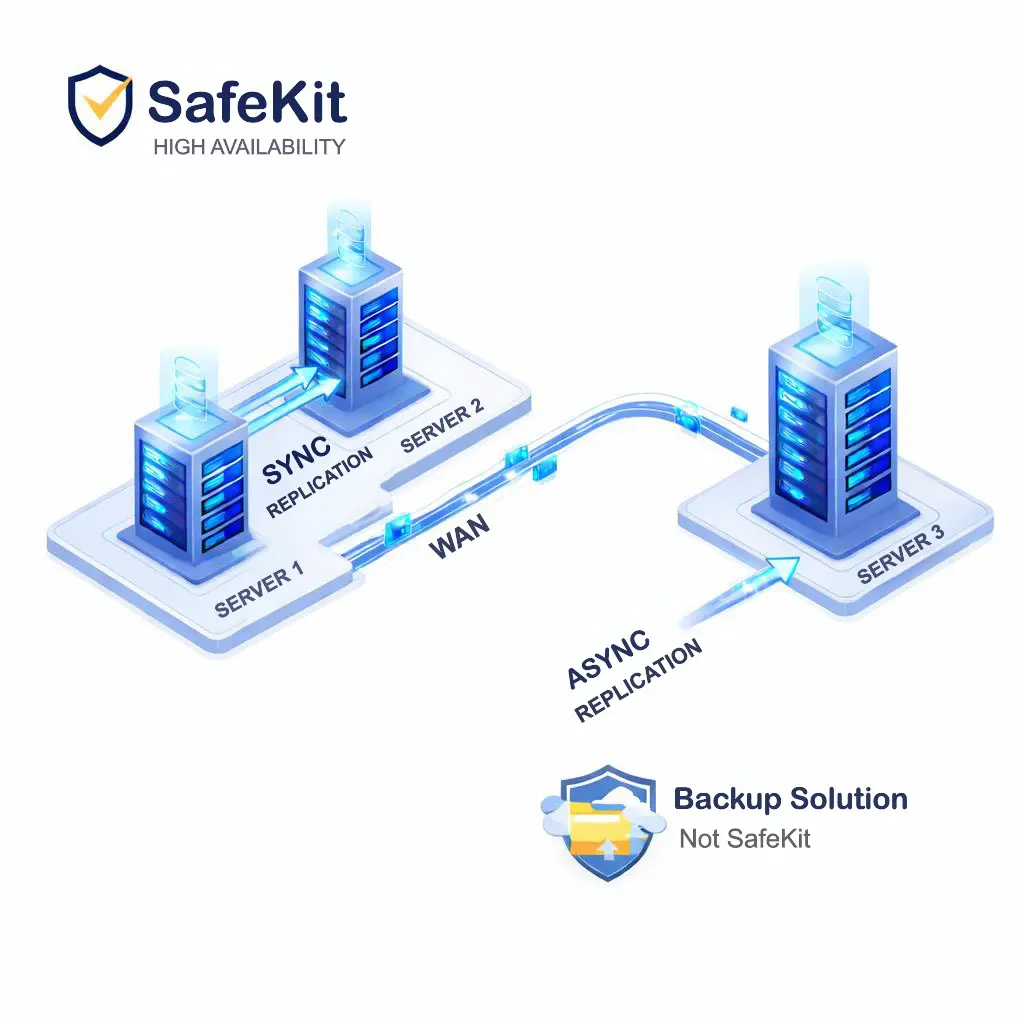
SafeKit provides a flexible, software-based High Availability and Disaster Recovery (HADR) architecture that eliminates the need for expensive shared storage. By implementing synchronous replication across a stretched VLAN between Server 1 and Server 2, SafeKit ensures that your critical applications remain "live" and consistent between two redundant sites.
To address the constraints of lower-bandwidth WANs, SafeKit is designed to be paired with backup and recovery solutions. This allows organizations to maintain 24/7 uptime through automatic failover while securing historical data for offsite disaster recovery.
Consequently, the environment is protected against hardware or software failures via SafeKit, and secured against logical errors and cyber threats like ransomware through the backup solution.
Synchronous HADR: Zero Data Loss over Fast Networks (LAN/VLAN)
How to implement HADR over a fast network?

To implement HADR over a fast network, deploy two nodes across remote sites to provide High Availability and Disaster Recovery simultaneously. This setup ensures that your application remains available even if an entire site fails, without the complexity of a shared storage infrastructure.
Why use a SANless HADR solution for fast networks?
A SANless solution like SafeKit is essential because it replicates data synchronously and in real-time between two nodes without shared disks. Because synchronous replication ensures zero data loss (RPO=0), the software can trigger an automatic application failover instantly if a hardware or software failure occurs.
What are the network requirements for Synchronous HADR?
Synchronous HADR requires an extended LAN or a stretched VLAN for three critical reasons:
- Virtual IP Failover: A single subnet is required to automatically failover the virtual IP address between nodes.
- Low Latency: Synchronous replication with no data loss typically requires a network round-trip time of less than 2ms.
- High Bandwidth: A connection of 1 Gb/s or more is required to ensure rapid data resynchronization during a failback.
Asynchronous HADR: Disaster Recovery over Slow Networks (WAN)
How to implement HADR over a slow network?
To implement HADR over a slow network (WAN), the architecture typically separates High Availability from Disaster Recovery. In this scenario, two nodes are deployed at the primary site for local redundancy, while a separate backup or asynchronous replication strategy is used to protect data at a distant remote site.
What is the best HADR solution for low-bandwidth connections?
The optimal solution involves deploying SafeKit at the primary site for local High Availability using synchronous real-time replication and automatic failover. For the disaster recovery site, data is protected via asynchronous replication or scheduled backups through the slow network, ensuring that local uptime is maintained without being bottlenecked by WAN latency. To achieve this architecture, a dedicated backup solution (other than SafeKit) is required to manage the data transfer and restoration at the remote site.How does failover work with a remote Disaster Recovery site?
Because asynchronous replication over a slow network involves potential data loss (RPO > 0), the failover process to a disaster recovery site is typically manual and managed by an administrator:
- Data Restoration: Backups are restored onto secondary servers at the DR site. Modern solutions like Veeam are often used to restore virtual machines (VMs) quickly to reduce recovery time.
- DNS Rerouting: Traffic is redirected to the DR site at the DNS level. The recovery time depends on DNS cache timeouts (TTL), and some client applications may require a restart to pick up the new IP address.
- Manual Decision: An administrator must verify data integrity at the remote site before authorizing the switch to the secondary data center.
How to Combine HADR and Backup for Total System Resilience
Comparing High Availability and Data Backup
Although both are critical for data protection, High Availability (HA) and Backup Solutions target different risks. High Availability, powered by SafeKit, provides a "live" failover mechanism to keep applications accessible during server outages or hardware failures. Conversely, a Backup Solution acts as a "historical" archive. While HA ensures 99.99% system availability by replicating data in real-time, backup focuses on data integrity, providing the necessary restoration points to recover from logical errors, accidental deletions, or ransomware attacks.
Is High Availability a substitute for a Backup strategy?
No, High Availability and backups are complementary, not interchangeable. While SafeKit ensures business continuity by keeping applications running during a hardware crash, it does not guard against logical errors, accidental deletions, or ransomware attacks. For example, because real-time replication mirrors every change instantly, a ransomware attack on the primary node will be immediately duplicated on the secondary node. To recover from such cyber threats or accidental deletions, you need a dedicated backup solution with a robust retention policy. This allows you to "rewind" your environment to a healthy state from before the corruption occurred.
Optimizing RTO and RPO: The Synergy Between HA and Backup
To build a truly resilient infrastructure, you must integrate both High Availability and backup into a unified strategy. These two technologies address different dimensions of the RTO (Recovery Time Objective) and RPO (Recovery Point Objective) equation:- High Availability (via SafeKit): Targets Instant Recovery. By maintaining a live, synchronous mirror of your environment, SafeKit achieves near-zero RTO and zero RPO. If a server fails, the application resumes on the secondary node immediately, ensuring no service interruption or data loss during the transition.
- Backup Solutions: Target Data Resilience. While HA keeps the service "live," backup creates an "immutable" history. It is your fallback for when the live data itself is compromised, allowing you to restore a clean version of your database from a specific point in time before a virus or accidental deletion occurred.
Comparison of HADR Architectures: Fast vs. Slow Networks
| Criteria | Fast Network (LAN/VLAN) | Slow Network (WAN) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Scope | Local Redundancy & High Availability | Site-to-Site Disaster Recovery |
| Use Case | Same Data Center or Campus | Remote Data Centers or Cloud Regions |
| Replication Type | Synchronous (Real-time) | Asynchronous / Backup |
| RPO (Data Loss) | Zero (RPO = 0) | Potential data loss (RPO > 0) |
| Failover Process | Automatic | Manual (Admin decision) |
| Traffic Rerouting | Virtual IP Address (VIP) | DNS Level (TTL dependent) |
| Latency Requirement | Low (typically < 2ms) | Supports high latency |
| Primary Recovery Goal | Immediate Business Continuity | Data Safety & Retention |
Video Guide: How to Implement HADR with SafeKit
🔍 SafeKit High Availability Navigation Hub
| Resource Type | Description | Direct Link |
|---|---|---|
| Key Features | Why Choose SafeKit for Simple and Cost-Effective High Availability? | See Why Choose SafeKit for High Availability |
| Deployment Model | All-in-One SANless HA: Shared-Nothing Software Clustering | See SafeKit All-in-One SANless HA |
| Partners | SafeKit: The Benchmark in High Availability for Partners | See Why SafeKit Is the HA Benchmark for Partners |
| HA Strategies | SafeKit: Infrastructure (VM) vs. Application-Level High Availability | See SafeKit HA & Redundancy: VM vs. Application Level |
| Technical Specifications | Technical Limitations for SafeKit Clustering | See SafeKit High Availability Limitations |
| Proof of Concept | SafeKit: High Availability Configuration & Failover Demos | See SafeKit Failover Tutorials |
| Architecture | How the SafeKit Mirror Cluster works (Real-Time Replication & Failover) | See SafeKit Mirror Cluster: Real-Time Replication & Failover |
| Architecture | How the SafeKit Farm Cluster works (Network Load Balancing & Failover) | See SafeKit Farm Cluster: Network Load Balancing & Failover |
| Competitive Advantages | Comparison: SafeKit vs. Traditional High Availability (HA) Clusters | See SafeKit vs. Traditional HA Cluster Comparison |
| Technical Resources | SafeKit High Availability: Documentation, Downloads & Trial | See SafeKit HA Free Trial & Technical Documentation |
| Pre-configured Solutions | SafeKit Application Module Library: Ready-to-Use HA Solutions | See SafeKit High Availability Application Modules |