Microsoft NLB in VMware: alternative to multicast and unicast with the SafeKit software
Evidian SafeKit
Microsoft NLB multicast mode
As explained in the knowledge base of VMware on network load balancing (NLB) multicast mode configuration, you need to manually configure static ARP resolution at the switch or router for each port that connects to the cluster. Deployment of the Microsoft NLB multicast mode in an unknown network environment can prove to be a complex and strenuous task.
Microsoft NLB unicast mode
With Microsoft NLB unicast mode, you must configure the ESXi/ESX host to not send RARP packets when any of its virtual machines is powered on. That's why, Microsoft NLB is not working properly in Unicast Mode with VMware.
Alternative with Evidian SafeKit
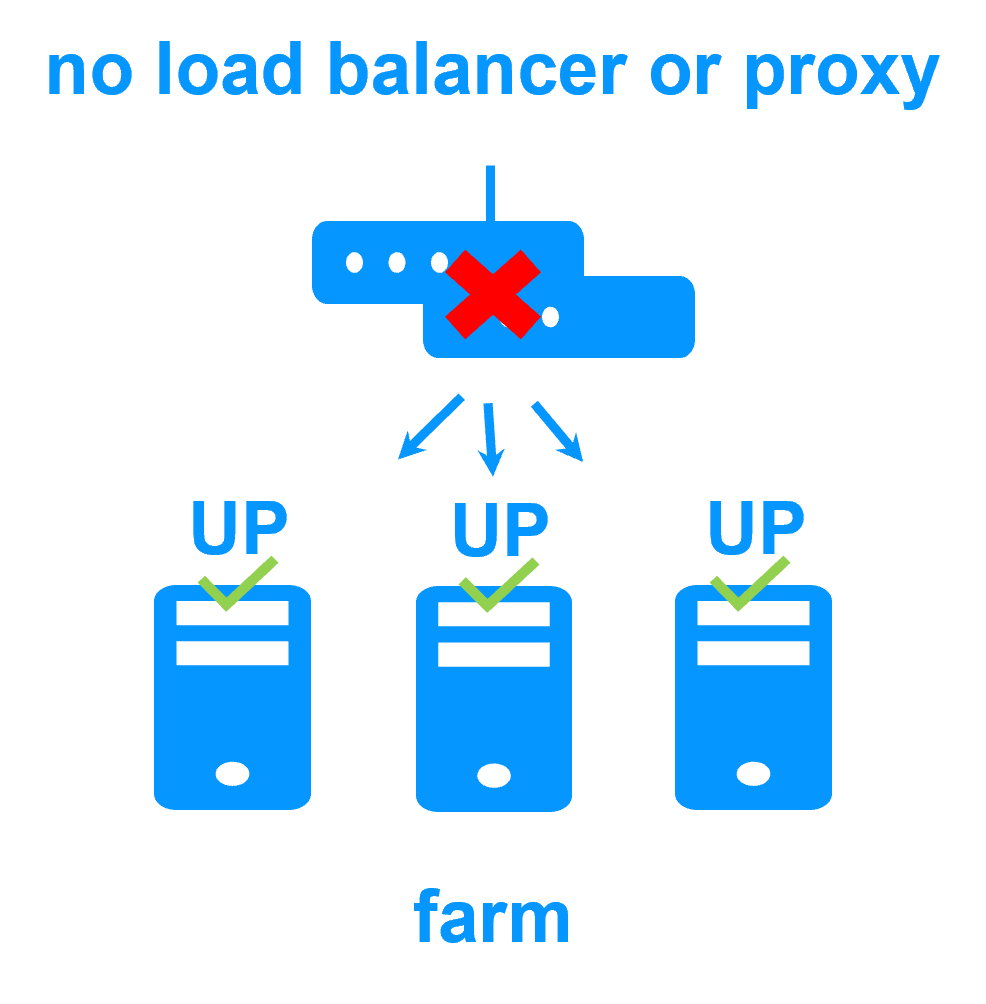
The SafeKit virtual IP address configuration does not require any special network configuration and the network load balancing can run in any environment. An important feature when the solution must be deployed in an unknown infrastructure: unknown switches or routers, physical servers or virtual servers.
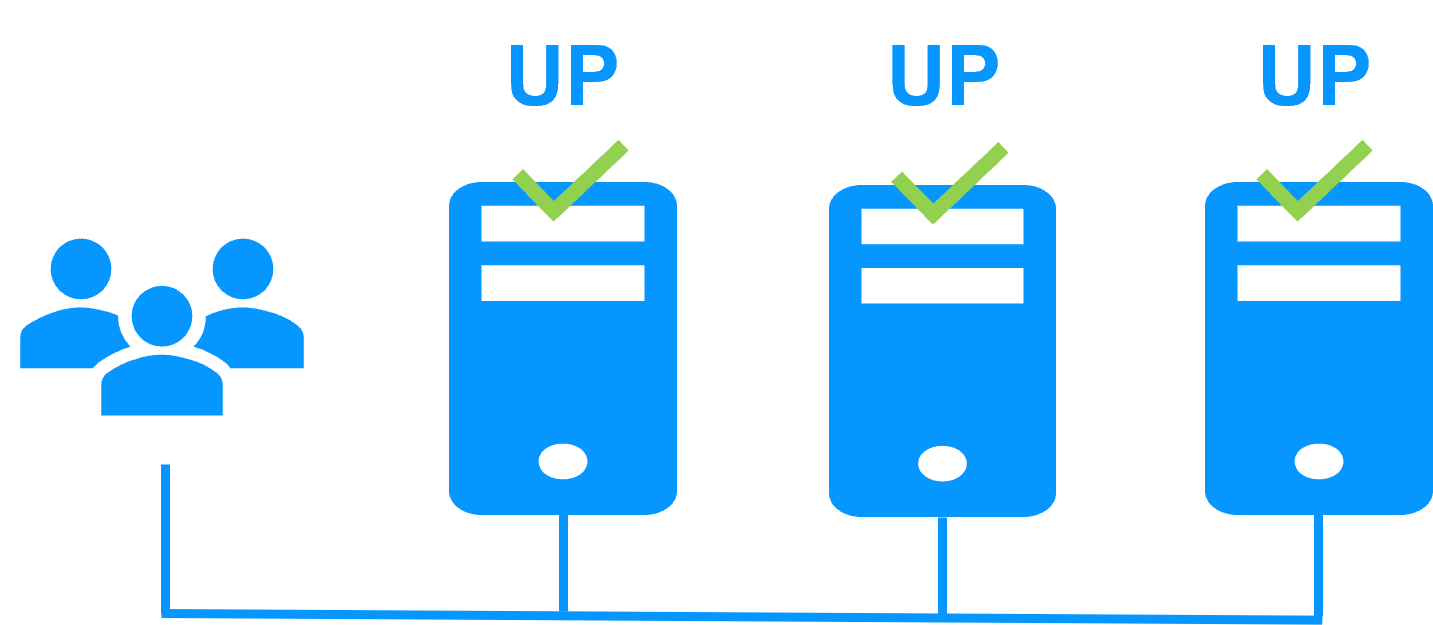
Virtual IP address in a farm cluster
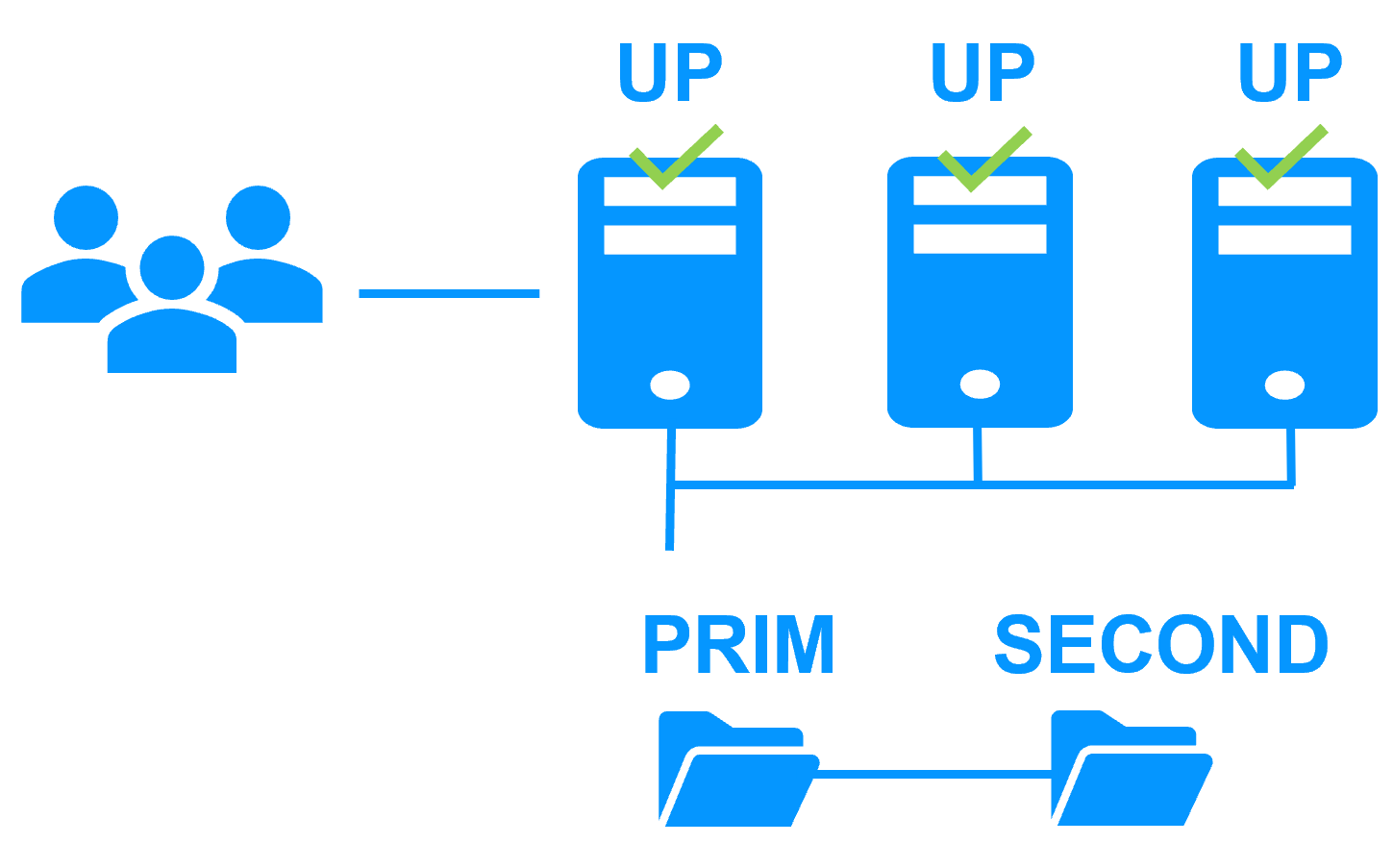
On the previous figure, the application is running on the 3 servers (3 is an example, it can be 2 or more). Users are connected to a virtual IP address.
The virtual IP address is configured locally on each server in the farm cluster.
The input traffic to the virtual IP address is received by all the servers and split among them by a network filter inside each server's kernel.
SafeKit detects hardware and software failures, reconfigures network filters in the event of a failure, and offers configurable application checkers and recovery scripts.
Load balancing in a network filter
The network load balancing algorithm inside the network filter is based on the identity of the client packets (client IP address, client TCP port). Depending on the identity of the client packet input, only one filter in a server accepts the packet; the other filters in other servers reject it.
Once a packet is accepted by the filter on a server, only the CPU and memory of this server are used by the application that responds to the request of the client. The output messages are sent directly from the application server to the client.
If a server fails, the SafeKit membership protocol reconfigures the filters in the network load balancing cluster to re-balance the traffic on the remaining available servers.
Stateful or stateless applications
With a stateful application, there is session affinity. The same client must be connected to the same server on multiple TCP sessions to retrieve its context on the server. In this case, the SafeKit load balancing rule is configured on the client IP address. Thus, the same client is always connected to the same server on multiple TCP sessions. And different clients are distributed across different servers in the farm.
With a stateless application, there is no session affinity. The same client can be connected to different servers in the farm on multiple TCP sessions. There is no context stored locally on a server from one session to another. In this case, the SafeKit load balancing rule is configured on the TCP client session identity. This configuration is the one which is the best for distributing sessions between servers, but it requires a TCP service without session affinity.
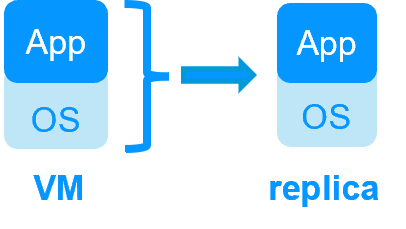
| VM HA with the SafeKit Hyper-V or KVM module | Application HA with SafeKit application modules |
 |
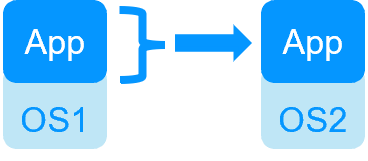 |
| SafeKit inside 2 hypervisors: replication and failover of full VM | SafeKit inside 2 virtual or physical machines: replication and failover at application level |
| Replicates more data (App+OS) | Replicates only application data |
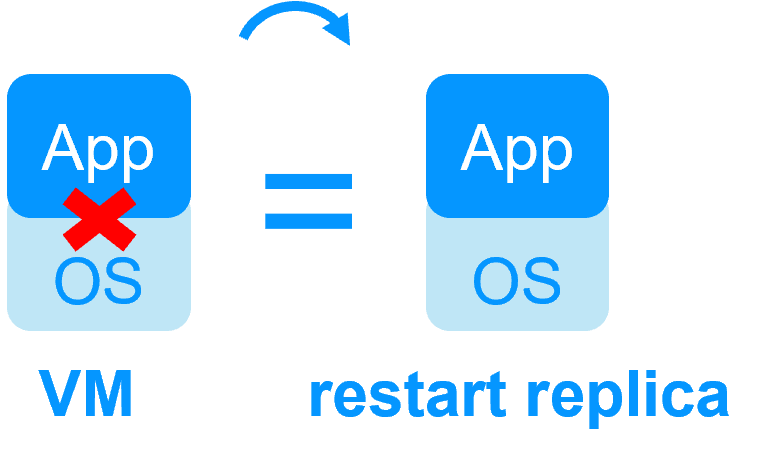
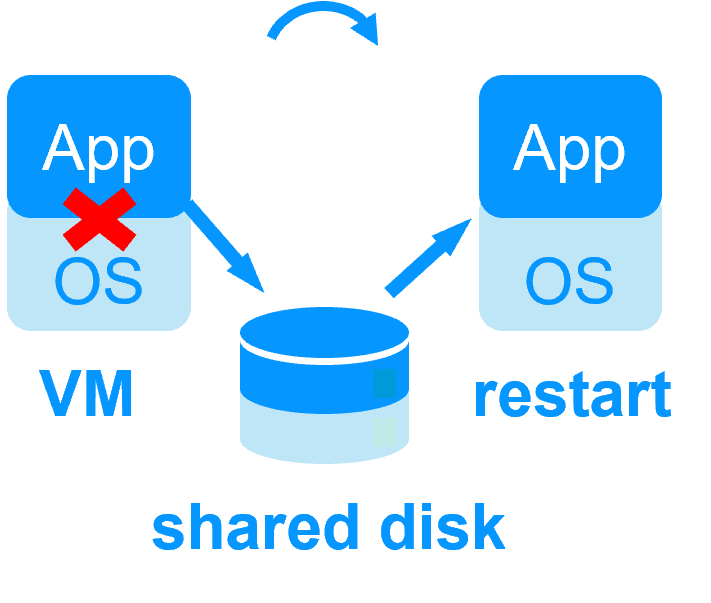
| Reboot of VM on hypervisor 2 if hypervisor 1 crashes Recovery time depending on the OS reboot VM checker and failover (Virtual Machine is unresponsive, has crashed, or stopped working) |
Quick recovery time with restart of App on OS2 if crash of server 1 Around 1 mn or less (see RTO/RPO here) Application checker and software failover |
| Generic solution for any application / OS | Restart scripts to be written in application modules |
| Works with Windows/Hyper-V and Linux/KVM but not with VMware | Platform agnostic, works with physical or virtual machines, cloud infrastructure and any hypervisor including VMware |
| SafeKit with the Hyper-V module or the KVM module | Microsoft Hyper-V Cluster & VMware HA |
 |
 |
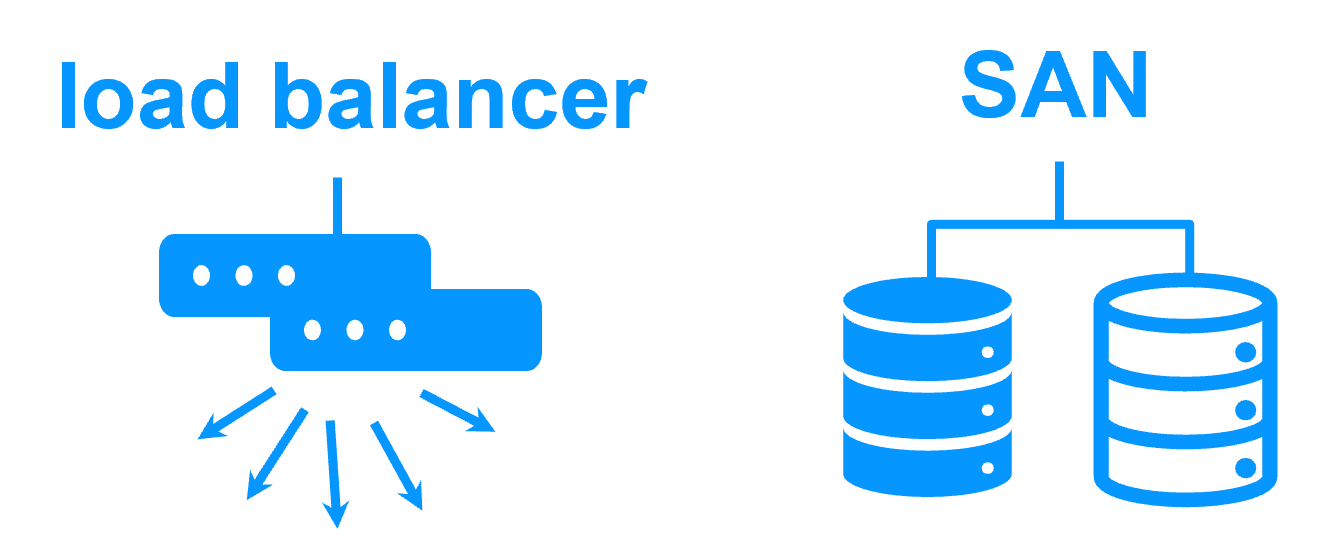
 No shared disk - synchronous real-time replication instead with no data loss No shared disk - synchronous real-time replication instead with no data loss |
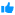
 Shared disk and specific extenal bay of disk Shared disk and specific extenal bay of disk |
 Remote sites = no SAN for replication Remote sites = no SAN for replication |
 Remote sites = replicated bays of disk across a SAN Remote sites = replicated bays of disk across a SAN |
 No specific IT skill to configure the system (with hyperv.safe and kvm.safe) No specific IT skill to configure the system (with hyperv.safe and kvm.safe) |
 Specific IT skills to configure the system Specific IT skills to configure the system |
| Note that the Hyper-V/SafeKit and KVM/SafeKit solutions are limited to replication and failover of 32 VMs. | Note that the Hyper-V built-in replication does not qualify as a high availability solution. This is because the replication is asynchronous, which can result in data loss during failures, and it lacks automatic failover and failback capabilities. |
Evidian SafeKit mirror cluster with real-time file replication and failover |
|
3 products in 1
More info >
 |
|
Very simple configuration
More info >
 |
|
Synchronous replication
More info >
 |
|
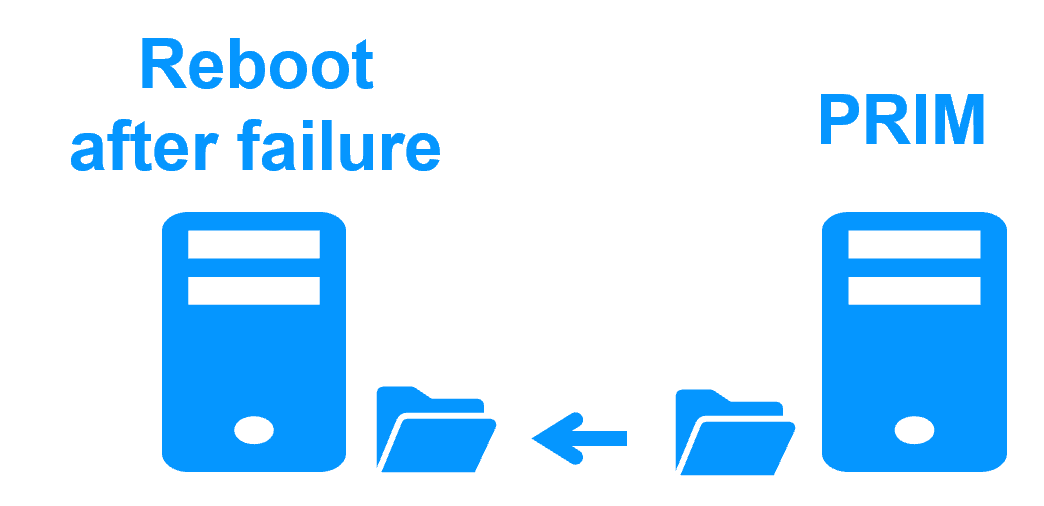
Fully automated failback
More info >
 |
|
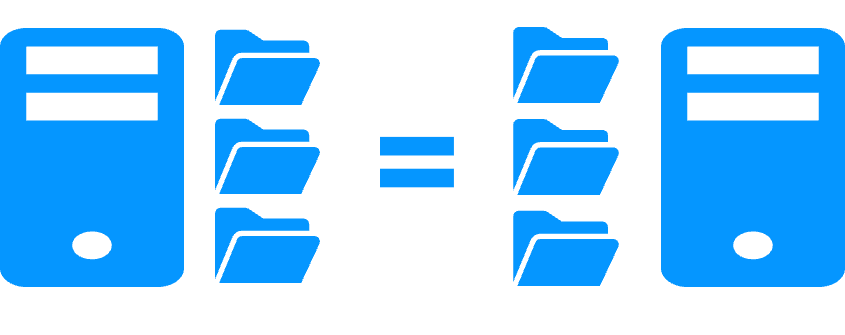
Replication of any type of data
More info >
 |
|
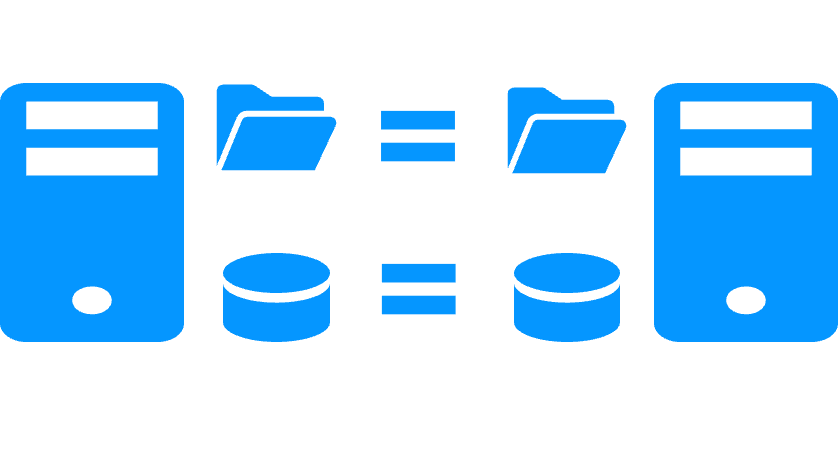
File replication vs disk replication
More info >
 |
|
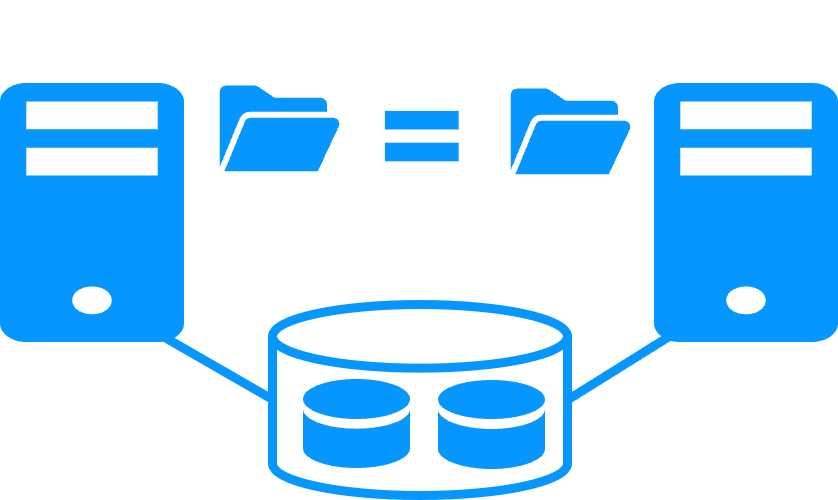
File replication vs shared disk
More info >
 |
|
Remote sites and virtual IP address
More info >
 |
|
Quorum and split brain
More info >
 |
|
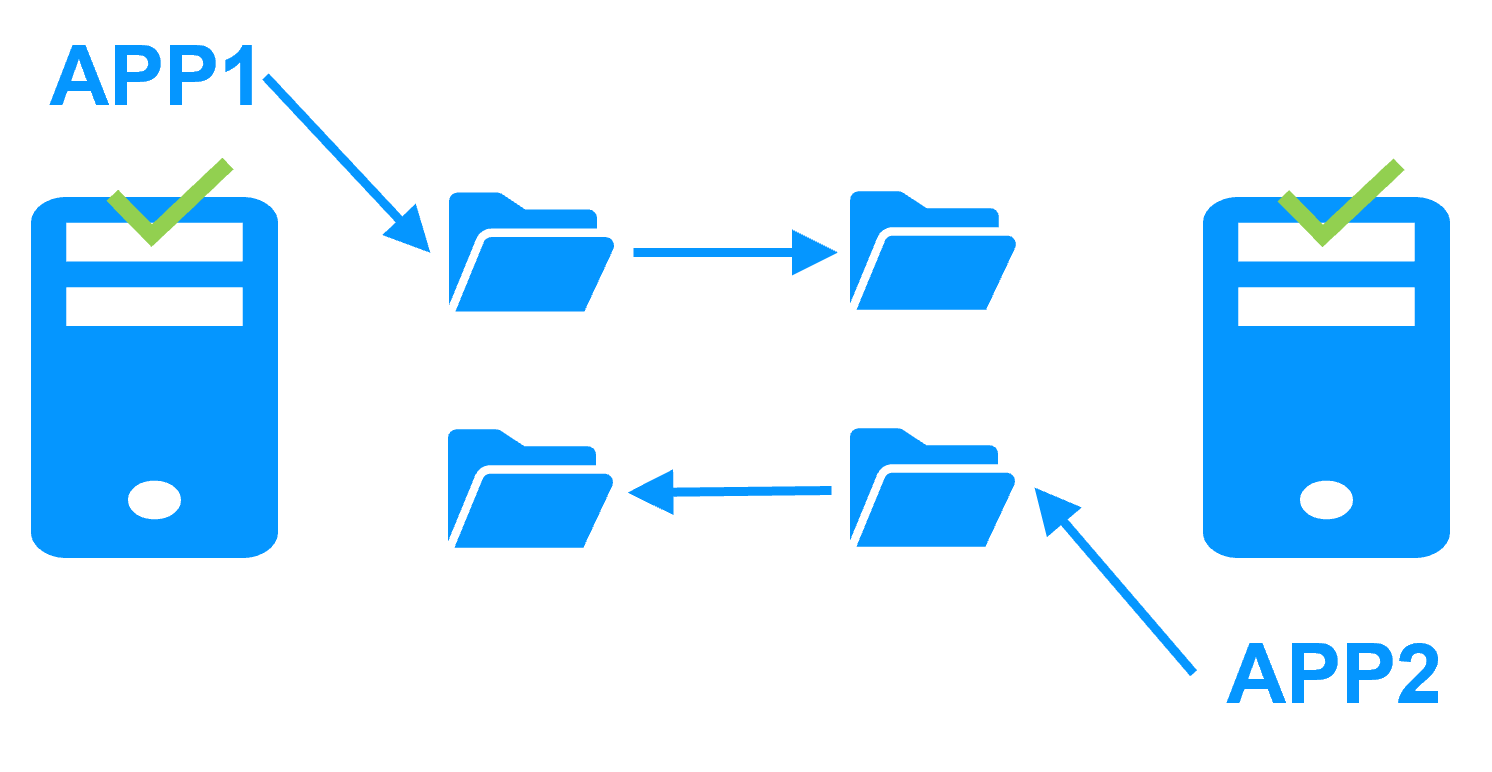
Active/active cluster
More info >
 |
|
Uniform high availability solution
More info >
 |
|
RTO / RPO
More info >
 |
|
Evidian SafeKit farm cluster with load balancing and failover |
|
No load balancer or dedicated proxy servers or special multicast Ethernet address
More info >
 |
|
All clustering features
More info >
 |
|
Remote sites and virtual IP address
More info >
 |
|
Uniform high availability solution
More info >
 |
|
Software clustering vs hardware clustering More info > |
|
|
|
Shared nothing vs a shared disk cluster More info > |
|

|
|
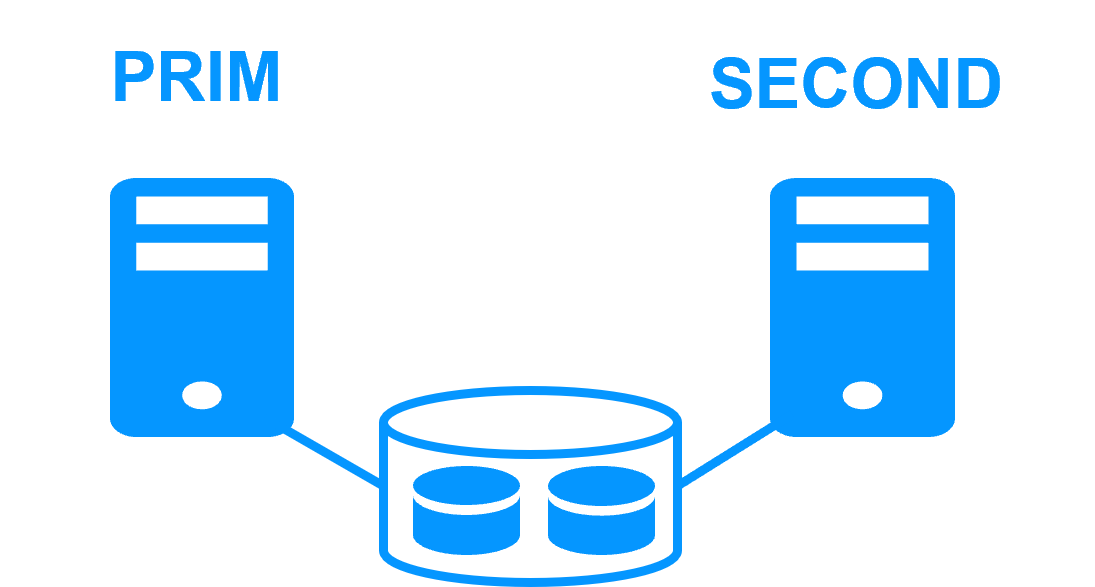
Application High Availability vs Full Virtual Machine High Availability More info > |
|

|

|
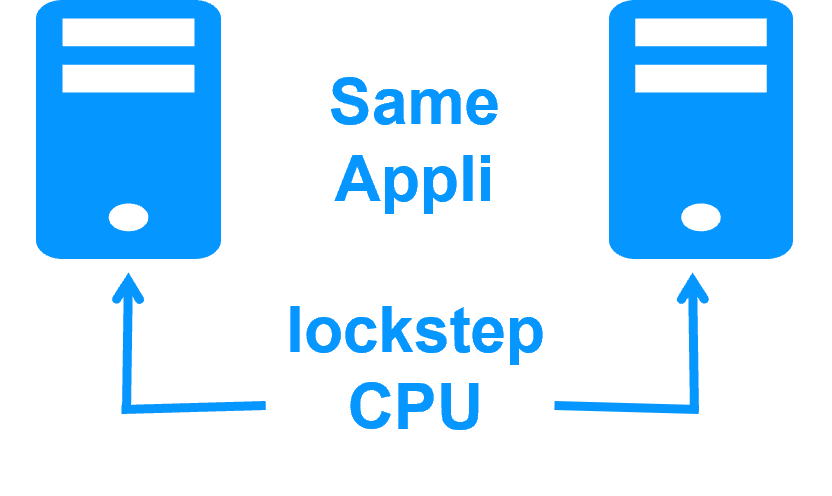
High availability vs fault tolerance More info > |
|

|
|
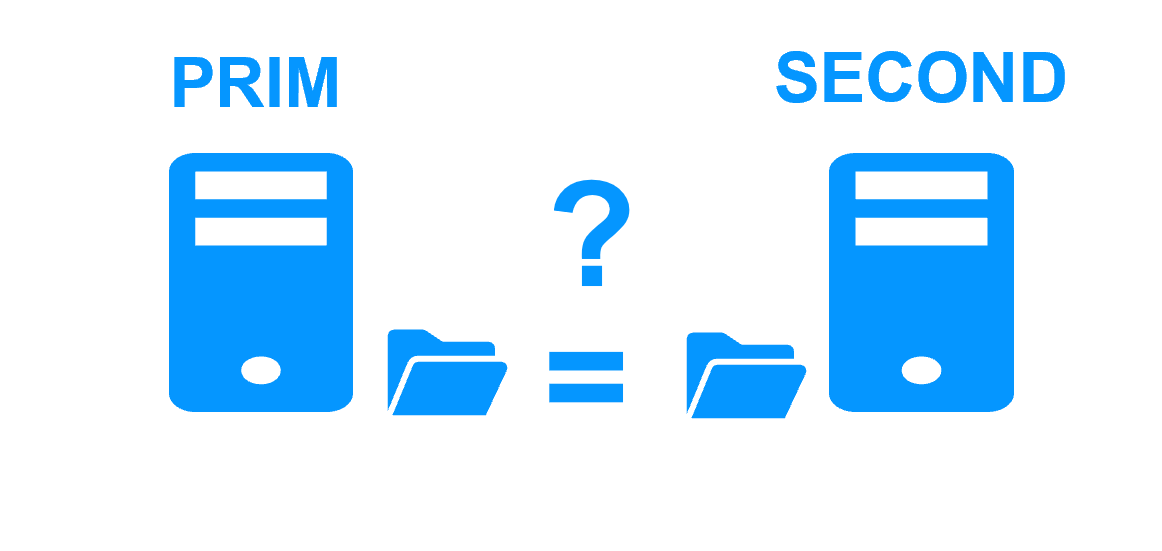
Synchronous replication vs asynchronous replication More info > |
|

|
|
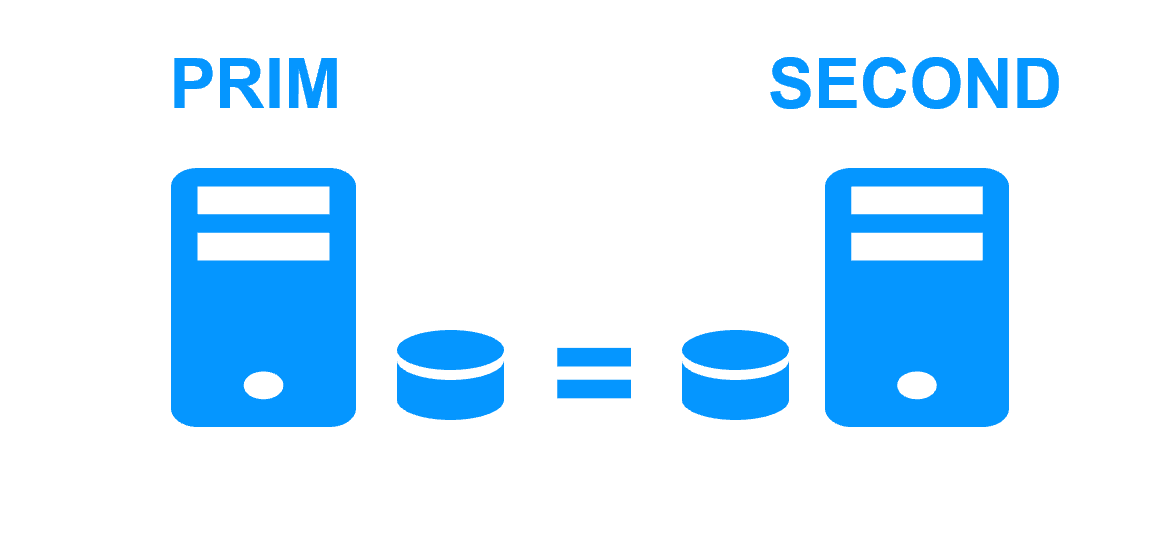
Byte-level file replication vs block-level disk replication More info > |
|

|
|
Heartbeat, failover and quorum to avoid 2 master nodes More info > |
|

|

|
Virtual IP address primary/secondary, network load balancing, failover More info > |
|
|

|
New application (real-time replication and failover)
- Windows (mirror.safe)
- Linux (mirror.safe)
New application (network load balancing and failover)
Database (real-time replication and failover)
- Microsoft SQL Server (sqlserver.safe)
- PostgreSQL (postgresql.safe)
- MySQL (mysql.safe)
- Oracle (oracle.safe)
- MariaDB (sqlserver.safe)
- Firebird (firebird.safe)
Web (network load balancing and failover)
- Apache (apache_farm.safe)
- IIS (iis_farm.safe)
- NGINX (farm.safe)
Full VM or container real-time replication and failover
- Hyper-V (hyperv.safe)
- KVM (kvm.safe)
- Docker (mirror.safe)
- Podman (mirror.safe)
- Kubernetes K3S (k3s.safe)
Amazon AWS
- AWS (mirror.safe)
- AWS (farm.safe)
Google GCP
- GCP (mirror.safe)
- GCP (farm.safe)
Microsoft Azure
- Azure (mirror.safe)
- Azure (farm.safe)
Other clouds
- All Cloud Solutions
- Generic (mirror.safe)
- Generic (farm.safe)
Physical security (real-time replication and failover)
- Milestone XProtect (milestone.safe)
- Nedap AEOS (nedap.safe)
- Genetec SQL Server (sqlserver.safe)
- Bosch AMS (hyperv.safe)
- Bosch BIS (hyperv.safe)
- Bosch BVMS (hyperv.safe)
- Hanwha Vision (hyperv.safe)
- Hanwha Wisenet (hyperv.safe)
Siemens (real-time replication and failover)
- Siemens Siveillance suite (hyperv.safe)
- Siemens Desigo CC (hyperv.safe)
- Siemens Siveillance VMS (SiveillanceVMS.safe)
- Siemens SiPass (hyperv.safe)
- Siemens SIPORT (hyperv.safe)
- Siemens SIMATIC PCS 7 (hyperv.safe)
- Siemens SIMATIC WinCC (hyperv.safe)