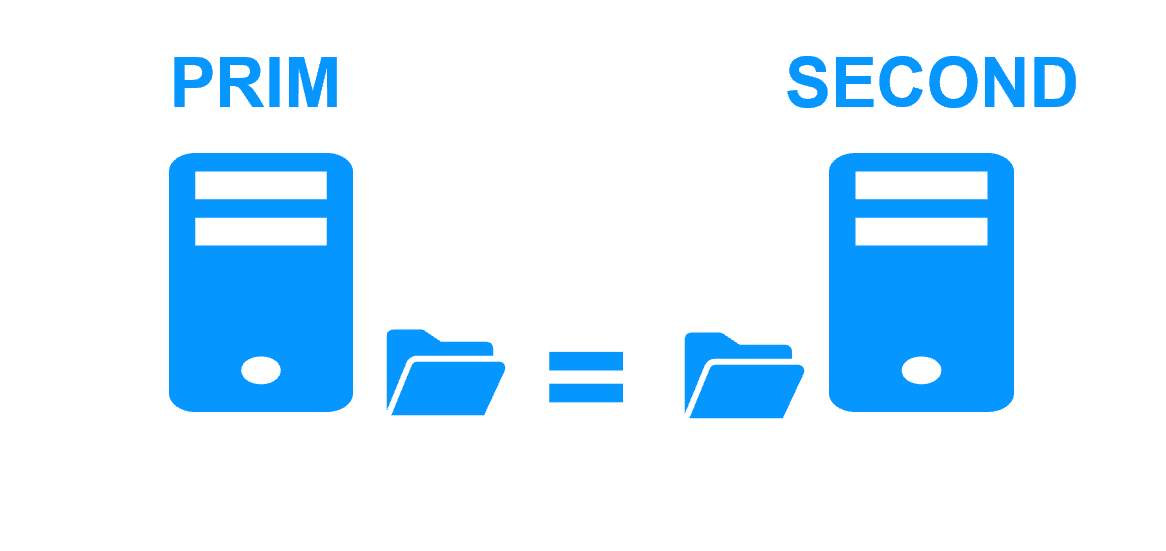
SafeKit mirror cluster with real-time file replication and failover
|
3 products in 1
More info >
|
- The SafeKit high availability software saves on Windows and Linux the cost of :
- external shared or replicated storage,
- load balancing boxes,
- enterprise editions of OS and databases
- SafeKit includes all clustering features: synchronous real-time file replication, monitoring of server / network / software failures, automatic application restart, virtual IP address switched in case of failure to reroute clients
|
Very simple configuration
More info >
|
- The cluster configuration is very simple and made by means of application modules. New services and new replicated directories can be added to an existing application module to complete a high availability solution
- All the configuration of clusters is made using a simple centralized web administration console
- There is no domain controller or active directory to configure as with Microsoft cluster
|
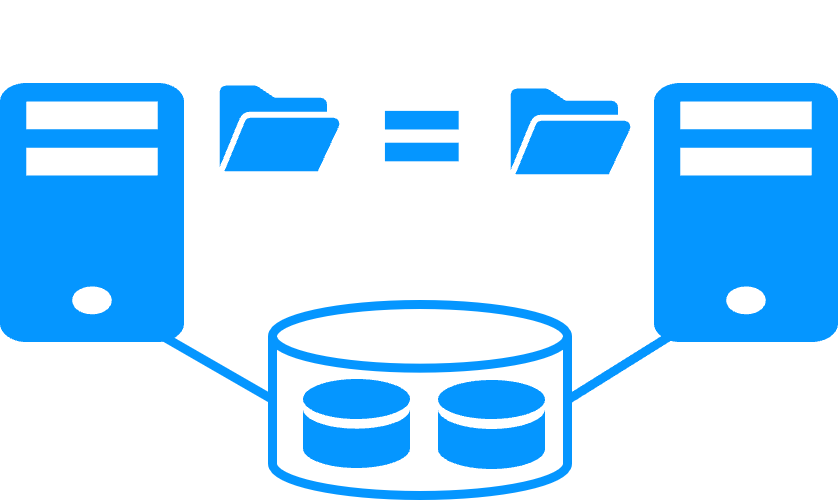
Synchronous replication
More info >
|
- The real-time replication is synchronous with no data loss on failure
- This is not the case with asynchronous replication
|
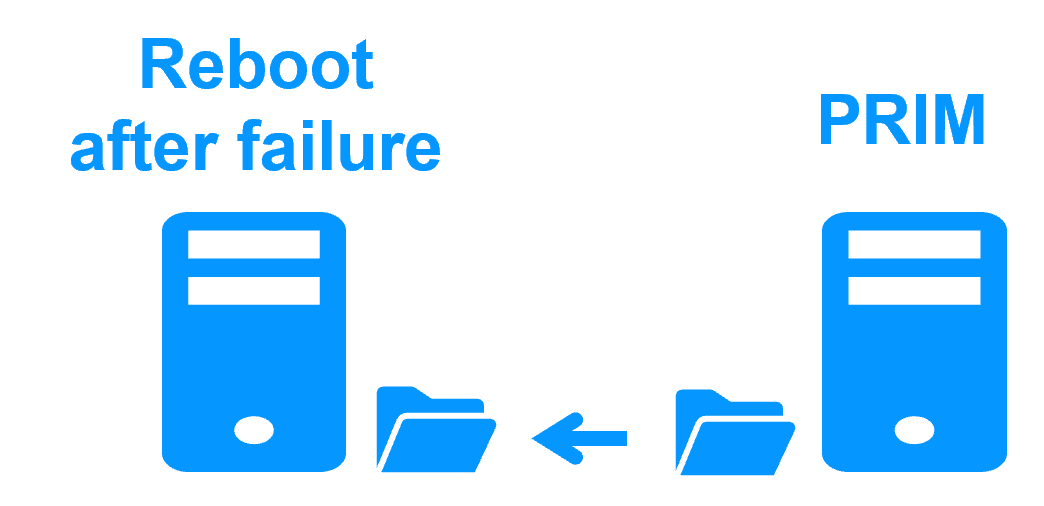
Fully automated failback
More info >
|
- After a failure when a server reboots, the replication failback procedure
is fully automatic and the failed server reintegrates the cluster without stopping the application on the only remaining server
- This is not the case with most replication solutions particularly with replication at the database level. Manual operations are required for resynchronizing a failed server. The application may even be stopped on the only remaining server during the resynchonization of the failed server
|
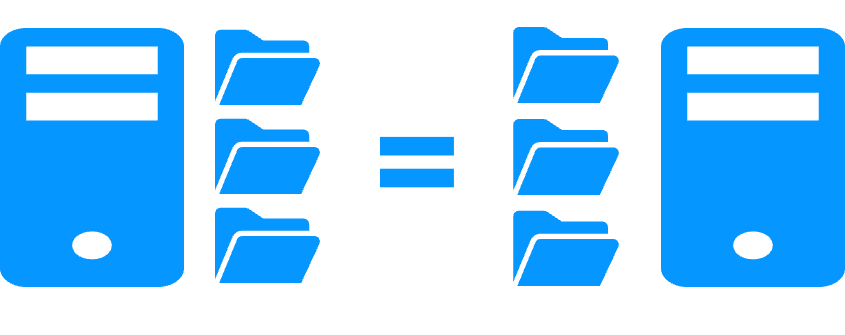
Replication of any type of data
More info >
|
- The replication is working for databases but also for any files which shall be replicated
- This not the case for replication at the database level
|
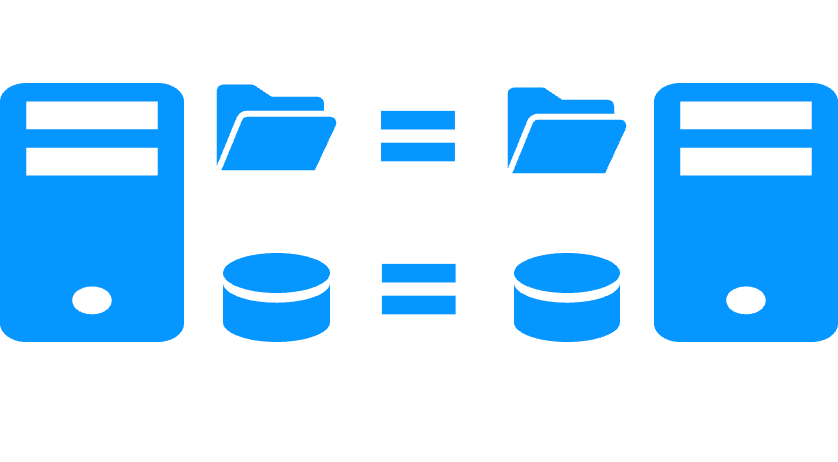
File replication vs disk replication
More info >
|
- The replication is based on file directories that can be located anywhere (even in the system disk)
- This is not the case with disk replication
where special application configuration must be made to put the application data in a special disk
|
File replication vs shared disk
More info >
|
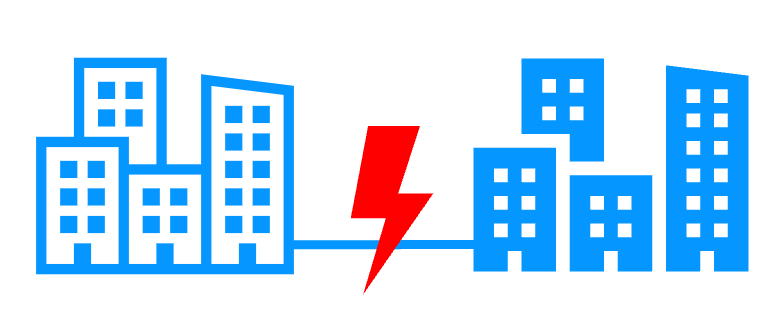
- The servers can be put in two remote sites
- This is not the case with shared disk solutions
|
Remote sites and virtual IP address
More info >
|
- All SafeKit clustering features are working for 2 servers in remote sites. Replication requires an extended LAN type network (latency = performance of synchronous replication, bandwidth = performance of resynchronization after failure).
- If both servers are connected to the same IP network through an extended LAN between two remote sites, the virtual IP address of SafeKit is working with rerouting at level 2
- If both servers are connected to two different IP networks between two remote sites, the virtual IP address can be configured at the level of a load balancer with the "healh check" of SafeKit.
|
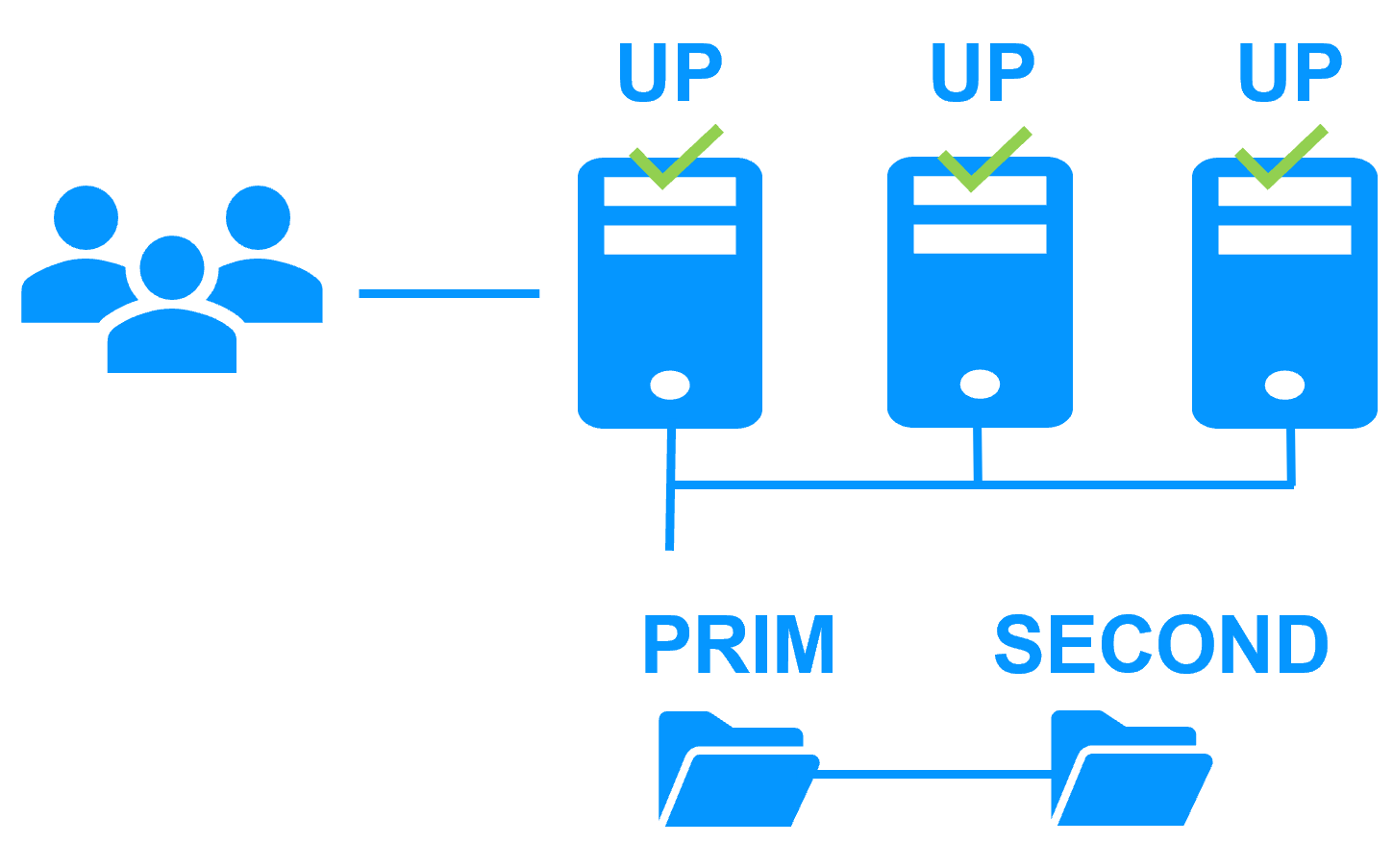
Quorum and split brain
More info >
|
- The solution works with only 2 servers and for the quorum (network isolation between both sites), a simple split brain checker to a router is offered to support a single execution of the critical application
- This is not the case for most clustering solutions where a 3rd server is required for the quorum
|
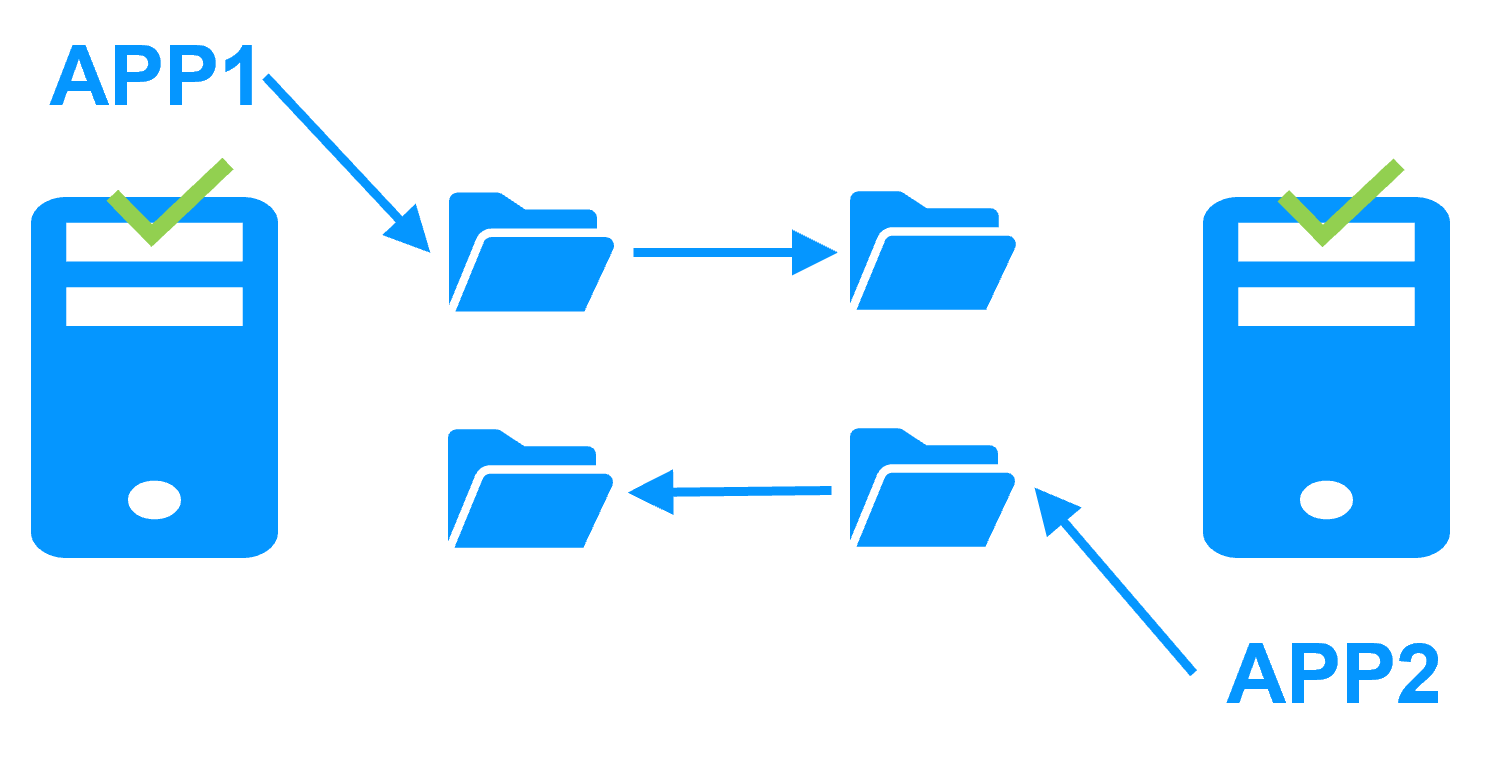
Active/active cluster
More info >
|
- The secondary server is not dedicated to the restart of the primary server. The cluster can be active-active by running 2 different mirror modules
- This is not the case with a fault-tolerant system where the secondary is dedicated to the execution of the same application synchronized at the instruction level
|
Uniform high availability solution
More info >
|
- SafeKit implements a mirror cluster with replication and failover. But it imlements also
a farm cluster with load balancing and failover.
- Thus a N-tiers architecture can be made highly available and load balanced with the same solution on
Windows and Linux (same installation, configuration, administration with the SafeKit console or with the command line interface). This is unique on the market
- This is not the case with an architecture mixing different technologies for load balancing, replication and failover
|
RTO / RPO
More info >
|
- SafeKit implements quick application restart in case of failure: around 1 mn or less
- Quick application restart is not ensured with full virtual machines replication. In case of hypervisor failure, a full VM must be rebooted on a new hypervisor with a recovery time depending on the OS reboot as with VMware HA or Hyper-V cluster
|